Insufficient blood supply to the heart, known as myocardial ischemia, can lead to symptoms such as chest pain, dizziness, and fatigue. This condition may lead to a myocardial infarction (so-called heart attack), one of the leading causes of ischemic heart disease. Currently available therapies for ischemic heart disease are symptomatic and do not cure or halt progression towards heart failure. Therefore, new therapies that can restore heart function, slow disease progression, and reduce post-heart attack complications are essential.
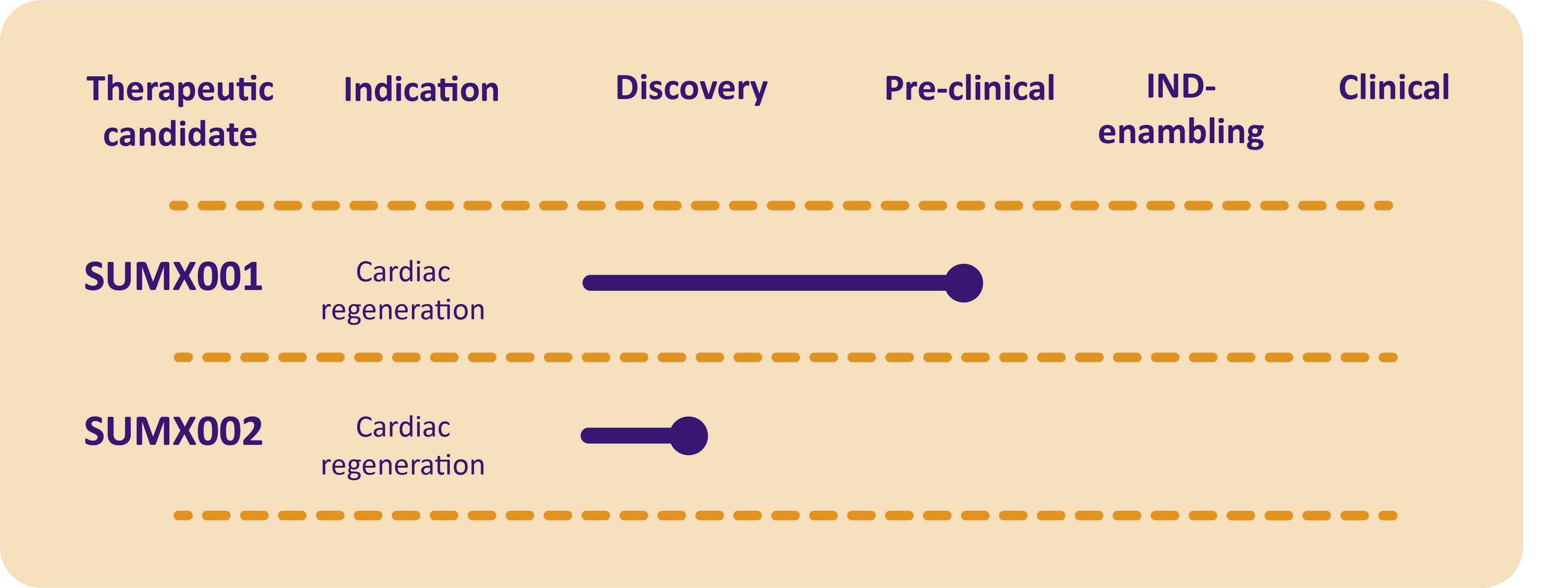
Research has shown that the adult human heart can replace its muscle cells, at a rate of about 0.5-1% per year. However, this rate is not enough to replace the millions of heart cells lost due to a heart attack. Fuelled by enthusiasm about the discoveries of activating proliferation of existing heart muscle cells and revascularisation of cardiac tissue, Summa currently develops two gene therapy approaches that elicit cardiac regeneration.